Your Cart is Empty
FREE SHIPPING ON ALL ORDERS $75+
HHC is edging its way into the hempmarket spotlight, but little is known about this new psychoactive hemp derivative. If you’ve just stumbled upon this shiny new cannabinoid, you’re likely asking yourself–what’s the difference in HHC vs THC?
It’s a great question, because HHC distinctly differs from THC, including hemp-derived THC products like Delta-8, Delta-10, and THC-O. It may even have a few extra benefits, like a more stable legal atmosphere and a better chance at evading common drug test methods.
All in all, it sounds like a win for consumers chasing a legal psychoactive experience, but we recommend you weigh all the pros and cons before jumping into the HHC market.
To help you get started, we’ll break down the difference between HHC and THC and how it impacts its legality, safety, dosage, and more. Let’s go:
HHC is a hemp-derived cannabinoid with psychoactive effects similar to THC, but the two compounds are inherently different.
HHC is slightly less potent than THC, but still induces strong psychoactive effects.
HHC is federally legal and can be purchased online, while most Delta-9 THC products must be bought in state-licensed dispensaries.

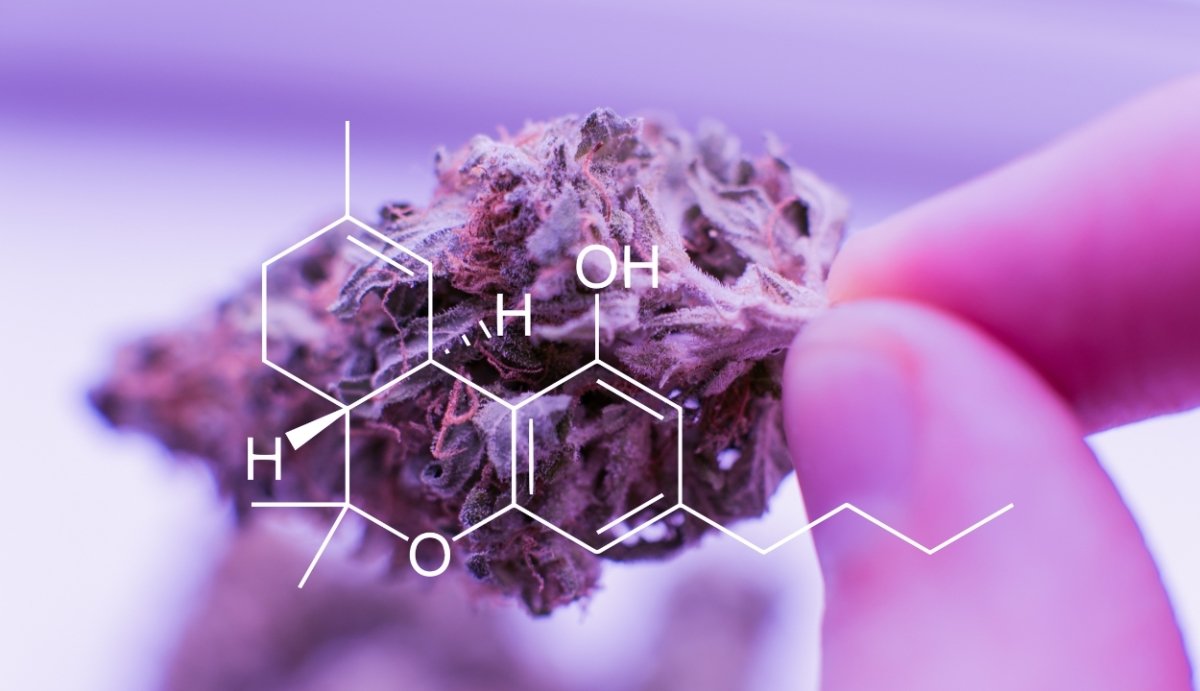
HHC, chemically known as “11-Hydroxyhexahydrocannabinol” or just “hexahydrocannabinol” is a hydrogenated THC analog that was discovered in the 1940’s by renown cannabis researcher Roger Adams–the same American chemist who isolatedCBD.
It’s a naturally occurringcannabinoid, although it’s usually found only in natural cannabis material in trace amounts, so most of the HHC found on the market today is synthesized from other cannabinoids derived from legal hemp material. This is similar to the way that Delta-8, Delta-10, and otherhemp-derived THC products are made and is the reason why HHC is federally legal, despite having potent psychoactive effects that are similar to Delta-9 THC’s effects.
Although HHC takes a form similar toTHC, it also includes a hydrogen atom, so it’s not technically classified as a THC molecule. HHC differs from THC molecules because it lacks double bonds. During the hydrogenation process used to create HHC, its double bonds are broken down and replaced with hydrogen molecules.
Although understanding these hydrogen bonds can be pretty complex, the most important thing to know is that HHC may have a slightly different affinity for both the CB1 and CB2 receptors than various forms of THC, including Delta-9 THC. Still, HHC does interact with the CB1 receptor responsible for inciting the psychoactive effects associated with THC, so HHC can incite some psychoactive effects of its own.

Yes! HHC is a psychoactive compound, soit will get you high, although the effects are a bit different from many of the THC products on the market. Many people enjoy HHC for recreational purposes, although it’s likely that it also has some therapeutic potential similar to THC. We’ll discuss the effects in greater detail down below.
Let’s dig into all the similarities and differences between HHC and THC:
In general, HHC is thought to be about 70-80% as strong as traditional THC (Delta-9-THC), meaning it’s even more potent than Delta-8-THC. This makes HHC a fair “middle ground” between the mild-mannered Delta-8 and full-strength THC products.
We want to clarify that by “potency” we mean the cannabinoid's affinity for the CB1 receptors in the brain, which is the cannabinoid receptor responsible for inducing psychoactive effects. The actual potency or intensity of effects you experience from a particular product has a lot to do with your personal THC tolerance, body weight, and the dosage that you take.
HHC has its own range of therapeutic effects that are usually described as being somewhat relaxing and sedating. Many people enjoy the middle ground between the mild, body-focused effects of Delta-8 and the potent, heady effects of Delta-9.
Because HHC is slightly milder than traditional THC, its thought to be less likely to induce some of thenegative side effects that are sometimes associated with THC, like anxiety and paranoia.
In general, the time frame for HHC’s effects is similar to that of most THC products. The effects of HHC and THC, when inhaled, may last between two and three hours. The effects may be more dependent on the dosing style used, and inhalation methods methods may have shorter-lived effects than edibles.
The legal realm is an area where HCC and THC greatly differ. HHC, which typically exists as a hemp product, falls under the the definition for legal hemp products used in the2018 Farm Bill, which means it’s legal by federal standards.
It’s important to note that HHC may not always be legal at the state level because some states have explicitly banned psychoactive hemp products. However, HHC often evades even state laws, which are commonly focused on “hemp-derived THC products,” because it is not technically a THC product. Determining where HHC is banned at the state level can be difficult, but you can learn more about hemp-derived THC laws by reading “Where is Delta 8 THC Legal? A State By State Guide to Delta-8 Laws.”
Delta-9-THC, however, is a cannabis product that’s federally prohibited, but is sometimes legal at the state level for either medicinal or recreational purposes.
Part of the appeal of HHC is that it may not trigger a positive drug test the same way that THC will. This is based mostly on anecdotal reports, but the premise is that HHC does not produce the same THC metabolites in the body as THC products because HHC is not a THC molecule.
Drug tests look for these THC metabolites, not THC, which may mean that HHC is a “workaround” for consumers subject to drug testing. Of course, this is highly debated and not necessarily evidence-based, so do your own research before taking the risk.
To learn more, read “Can HHC Make You Fail a Drug Test?”
Delta-9-THC can typically only be bought in state-licensed dispensaries in states where cannabis is legal for either recreational or medical use. HHC, on the other hand, is available online and can be shipped directly to your door.
As far as variety goes, you're currently more likely to find a wide variety of Delta-9 products in dispensaries than you’ll find for HHC when shopping online. That’s simply because HHC is still very new and only a few manufacturers have mastered the techniques used to create high-quality HHC products.
You can find Delta-9 edibles, flower, vapes, softgels, and more in state-licensed dispensaries. You may be able to find some of the same dosing styles for HHC formulas as well, but you'll most commonly find HHC as a vape or edible. In some cases,HHC products also contain THC, Delta-8, THC-O, or other hemp-derived THC compounds as well, so be sure to read the label carefully.

The way that HHC vs THC is made is a defining factor between the two cannabinoids, mainly because THC is naturally derived from cannabis material while HHC needs to be synthesized in a lab.
To explain the difference briefly, THC naturally exist in cannabis material and can be easily extracted or simply enjoyed by smoking cannabis flower. HHC naturally exists in cannabis flower, too, but in trace amounts that are not useful for extraction.
Instead, HHC is created by a process called “hydrogenation,” the same process used to convert vegetable oil to margarine. This process involves adding hydrogen molecules to THC to change their structure, but does not require adding or removing any other synthetic substances. The final result is an HHC molecule that is identical to the HHC molecule available naturally in the plant.
It’s important to note that although HHC is a “synthetic cannabinoid,” it differs greatly from K2, spice, or other versions of synthetic cannabinoids you may find on the street market. These synthetic products are illegal and potentially dangerous, and they are generally not made from real plant material at all.
Because HHC is synthesized, its safety often comes into question when comparing it to THC. Currently, there's no evidence that proves that HHC is unsafe. In some cases, HHC may be considered a safer option by default simply because it's not as potent, so the potential of overdoing it is much lower.
For now, research regarding the safety of HHC, especially with long-term use, is limited. The same is true for most hemp-derived cannabinoids, which are still largely unregulated. Of course, many experts believe that the risk and benefit profile of HHC is similar to that of traditional THC, meaning it may be safe when used responsibly and in moderation.
As with all hemp-derived cannabinoid products, the most significant risks come from purchasing low-quality, contaminated products. Because regulations are inconsistent from state to state, it’s crucial for consumers to do their due diligence when shopping for HHC and other hemp products.
Look for a company that uses clean, high-quality hemp material and safe manufacturing procedures. A trustworthy hemp manufacturer will always provide third-party lab test reports for their products, and you can use those tests to verify the absence of pesticides, mold, and other contaminants, or to verify the potency as presented on the product label.
It's hard to compare the average dosage of THC and HHC because dosage size generally depends on many unique factors, like tolerance, body weight, and desired effects.
In general, the dosage thresholds for THC and HHC are incredibly similar, and an average dose for either is around 25 milligrams. For milder effects, you may use doses as low as 5-10 milligrams, and experienced THC consumers may prefer doses of 50 milligrams or higher.
There may be some slight variation because HHC is slightly less potent, but you’ll need to try it for yourself to figure out the best dosing threshold because everyone’s experience varies.
As always, we recommend starting with small doses and working your way up in order to safely explore the HHC or THC experience.
Again, it’s hard to explore the different price points between HHC and THC simply because THC is subject to the prices set by the state market.
In states with established cannabis markets, you can often buy high-quality THC flower for less than $10 a gram, while it may cost nearly double that in other states with newer cannabis programs or a higher cost of living. THC products purchased at a dispensary are also subject to a special state tax, so they may cost a bit more than the ticket price.
However, the price for HHC products is comparable to the price for hemp-derived THC products, and both are often less expensive than high-THC cannabis products bought in a dispensary. One primary benefit to HHC is that you can buy it online, so its much easier to price shop and ensure you’re getting the most bang (and the best quality) for your buck.
|
Pros |
Cons |
|
|
Thanks to its natural hemp source, HHC is federally legal and legal in many U.S. states, which means it's far more accessible than traditional cannabis products. It's important that you source from trustworthy hemp manufacturers that provide third-party lab tests for every batch.
For now, HHC may be more difficult to find than THC-O, Delta-8, or other hemp derivatives. If you’re looking for legal hemp-derived THC you can order online that meets the most stringent quality standards, check out ourElev8 Collection.

HHC is estimated to be about 75–80% as potent as Delta-9-THC. It offers psychoactive effects that are milder and more relaxing, falling somewhere between Delta-8 and Delta-9 in strength.
Yes, Delta-9-THC is slightly stronger than HHC. However, the effects are similar, and both cannabinoids share comparable dosage thresholds.
HHC may be less likely to trigger a positive result on standard THC drug tests, but there's no guarantee. Some drug tests may detect THC analogs, so caution is advised if drug testing is a concern.
Delta-9 is the primary psychoactive compound in cannabis, while HHC is a hydrogenated analog with a slightly different structure. HHC produces similar effects but is generally milder and is often legally available in more regions.
HHC is federally legal under the 2018 Farm Bill and is permitted in many U.S. states. However, legality may vary by state, so always check local laws before purchasing.
Yes, HHC does produce a psychoactive high. Many users describe it as smoother, more clear-headed, and less anxiety-inducing than Delta-9-THC.
HHC is often used recreationally for its mild psychoactive effects and may offer therapeutic benefits like pain relief, mood elevation, and relaxation. More research is needed to confirm its full potential.
Comments will be approved before showing up.